Menopausal Disorder
Menopausal Disorder
Menopausal disorder refers to a variety of symptoms caused by a decrease in female sex hormones due to aging. Menopause occurs when menstruation is interrupted for more than a year due to the degeneration of the ovaries and the rapid decrease in female hormone secretion.
The symptoms include abnormality in the menstrual cycle due to deficiency of female sex hormones and atypical uterine bleeding, decreased vaginal discharge, decreased libido, urinary incontinence, etc.
Additionally, musculoskeletal symptoms such as joint pain, lower back pain, and shoulder pain occur. In the circulatory system, symptoms such as limb numbness, headache, and dizziness are present. On the other hand, the psychological symptoms include anxiety,rustration, and insomnia. The signs in the digestive system include indigestion, heartburn, constipation, and diarrhea.
These menopausal symptoms appear within two years before and after menopause and can last for about 3 to 5 years. However, the degree of difference varies from person to person, and not all patients are treated. About 25% of patients who experience severe symptoms require treatment. Also, about 20% of women have more severe menopausal symptoms, accompanied by hot flushes and anxiety, depression, memory loss, etc. The sleeping disorder could also occur if the symptoms mainly appear at night.
Symptoms of menopausal disorder
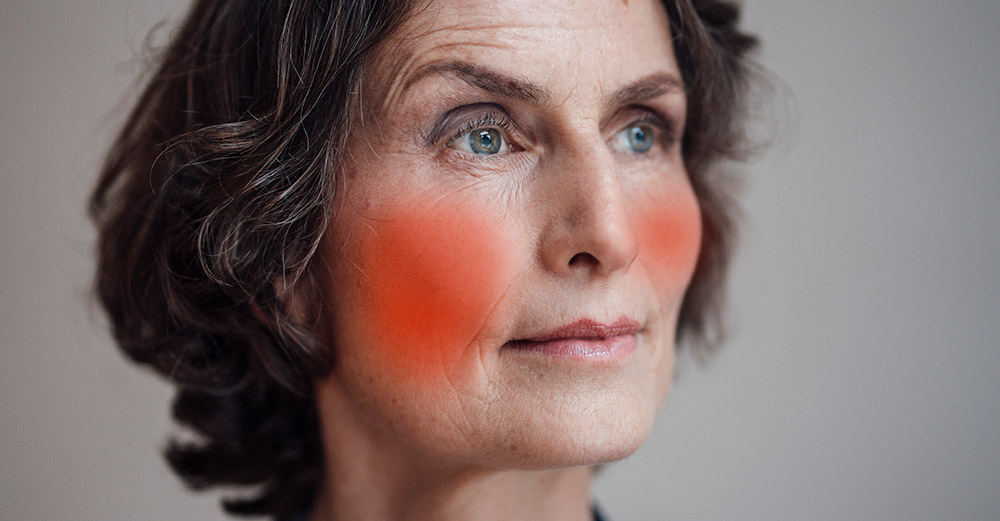
When you get stressed, cortisol prevents the absorption of serotonin, leading to serotonin depletion. Melatonin converts into serotonin under the sun. If you do not have enough serotonin, your body can suffer from hypothermia. Our body must maintain a body temperature of 98.6 Fahrenheit to be able to do vital activities.
The sensor of maintaining body temperature is in the hypothalamus, which keeps our body within one or two degrees of 98.6 degrees.
The hypothalamus works with other body temperature-regulating systems, such as the skin, sweat glands, and blood vessels.
If we do not have enough serotonin, our body temperature can drop.
When our body temperature drops, our heart, nervous system, and other organs cannot work correctly, and it is a risk for our body. The sympathetic nerve is activated to prevent it—our body secrets norepinephrine, which promotes heat generation. When norepinephrine is released, the fever rises rapidly, and when the fever goes off, it can get cold sweating, and our body feels cold.
Kynurenine connects to inflammation (viral infection, bacterial infection, autoimmunity, etc.). If inflammation occurs in our body, serotonin converts to Kynurenine, and Kynurenine produces niacin.
Excessive niacin can lead to hot flushes due to the extension of capillaries.
Therefore, hot flashes are not simply treated with female hormones but need to balance various hormones such as cortisol, serotonin, and thyroid.

-
Irritability
-
Feelings of sadness
-
Anxiety
-
Mood swing
-
Short memory loss
-
Lack of motivation
-
Aggressiveness
-
Difficulty concentrating

Menopausal syndrome Questionnaire
| No | Symptoms | Scoring | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absent | Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||
| 1 | Hot flushes and sweating | 0 | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| 2 | Numbness and tingling on hand or feet | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| 3 | Sleep problems | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| 4 | Anxiety, nervousness | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| 5 | Depression | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 6 | Dizziness | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 7 | Physical and mental Fatigue | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 8 | Joint and muscle pain | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 9 | Headache | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 10 | Palpitation | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 11 | Vaginal Dryness | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
Total 5~10 : mild / 10~15 : Moderate / >15 : Severe
MBR Menopausal Disorders Treatments
During menopause, women run into many problems due to hormonal imbalances.
MBR Acupuncture & Herb help minimize menopausal disorders with excellent therapeutic effects using herbal medicines, acupuncture, and moxibustion as a more natural remedy than synthetic hormones.

In Chinese medicine, menopause classifies the causes into three types: Kidney Deficiency (腎虛-congenital weakness), liver Qi Stagnation (肝氣鬱), and Heart and Spleen deficiency (心脾兩虛).
Among them, Kidney deficiency is the most. Due to aging, women are depleted of Jing(Kidney essence) and blood, leading to hormonal deficiency.
Herbal medicines can help hormone production and make calm the spirits.
MBR herb can obtain excellent effects in improving menopausal symptoms without side effects.
The ovaries and adrenal glands produce female hormones.
When menopause, ovarian function declines, and adrenal glands become the primary source of female hormone.
The jaw affects cervical vertebrae 1 and 2 and the torsion of cervical vertebrae 1 and 2 affects the neck structure and circulation of blood to the brain.
HPA axis is the most important axis for regulating hormones in our body. It increases the circulation of blood flow in the brain that regulates the ability of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to produce hormones. In relation, the female hormones are involved in the production the ovaries and adrenal glands. Treatment of the MBR mandibular joint improves not only the movement but also the imbalance of the human anatomy.

During menopause, the core body temperature decreases, and the body increases the norepinephrine to raise the core body temperature, which causes symptoms such as hot flushes.
Warming the lower abdomen with moxa and tonifying Kidney Yang with MBR herbal medicine prevent a decrease in the core body temperature.
In addition, a study shows moxibustion treatment has an excellent effect on reducing pain caused by osteoporosis and increasing bone density.