10step body exams
& 12meridian
for pain analysis
We observe the balance from head to toe.
10step body exams
& 12meridian
for pain analysis
We observe the balance from head to toe.
What is MBR body posture & 12 meridians analysis exam?
The 12 meridians that connect the 11 systems of the human body are connected from head to toe like a spider’s web.
Because these 12 meridians are distributed in the musculoskeletal system that moves the body, the balance of the 12 meridians can be easily analyzed quickly and objectively by examining the postures of the limbs, trunk, and craniofacial.
Externally, 12 Meridians are distributed in the primary channels and the sinew channels of the extremities, trunk, and craniofacial areas.
Internally, 12 Meridians are connected to the internal organs of the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, stomach, large intestine, and small intestine.
The 12 meridian balance examination investigated by posture and movement is a critical analyzation that can examine even the imbalance of internal organs.
The MBR meridian examination system is built based on numerous clinical results consisting of 10 steps over a long period.
From the result, a presumptive diagnosis of the root cause of pain, treatment prognosis, detailed treatment methods, and treatment design are made.
01
Standing
P to A
02
Standing
foot & ankle
03
Standing
lateral
04
Standing
Flx-Ext-SB
05
Standing
position1
06
Seated
position2
07
TMJ
assessment
08
Supine
position1
09
Static
palpation
10
Prone
position
We identify the relative positions of various joints and body segments from head to toe through a defined test regime Based on 20 years of clinical experience and numerous pain treatment studies, the 10-step test can quickly identify the cause of body imbalance as well as show visual improvement by comparing the test results after the treatment.
01
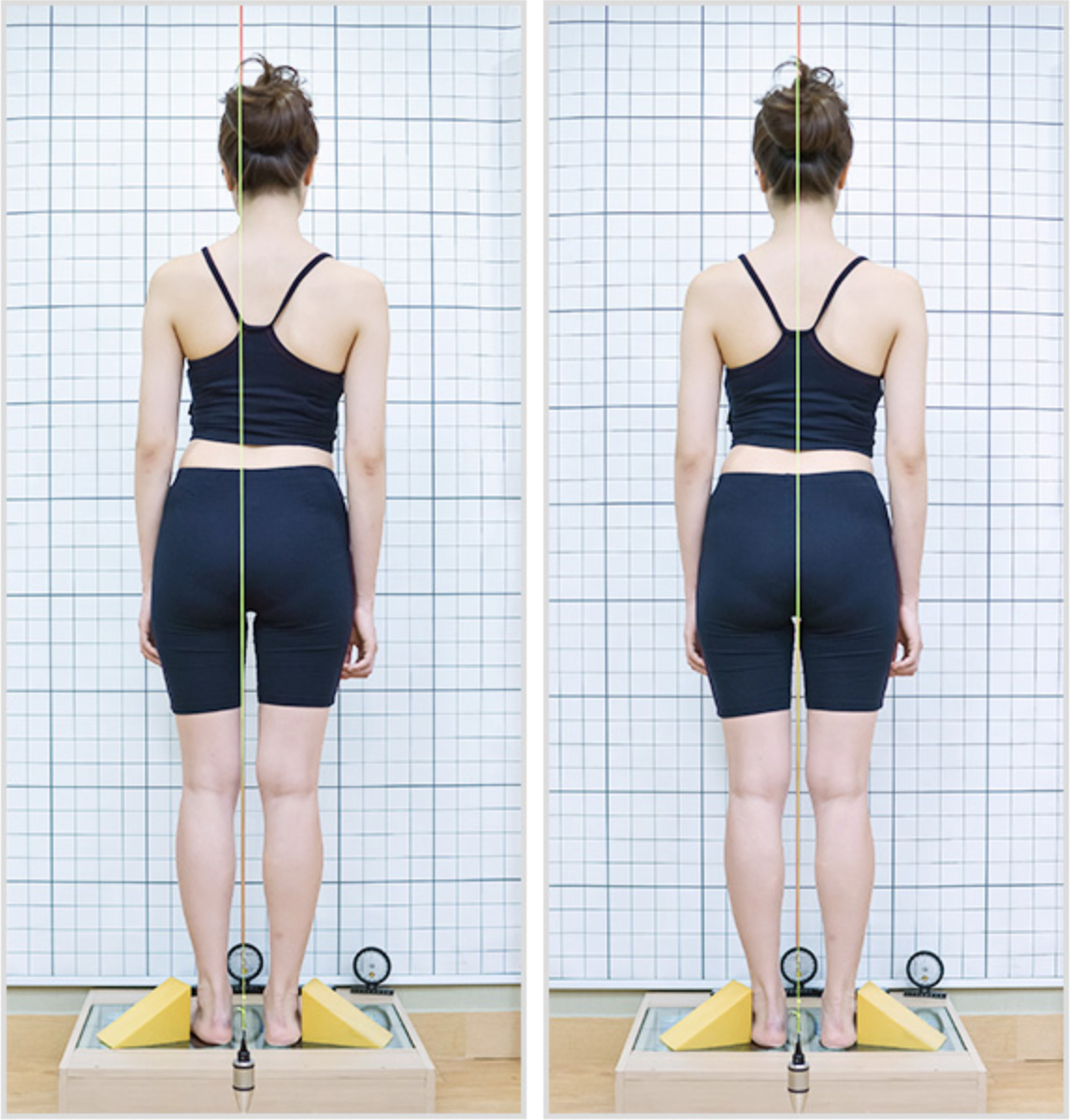
Posterior View
Posterior posture examination is the most important posture examination.
By identifying the positions of each joint from head to toe, the doctor can check the joint’s imbalance and the interrelationship of muscles. This test predicts what the next posture screening should focus on.
02
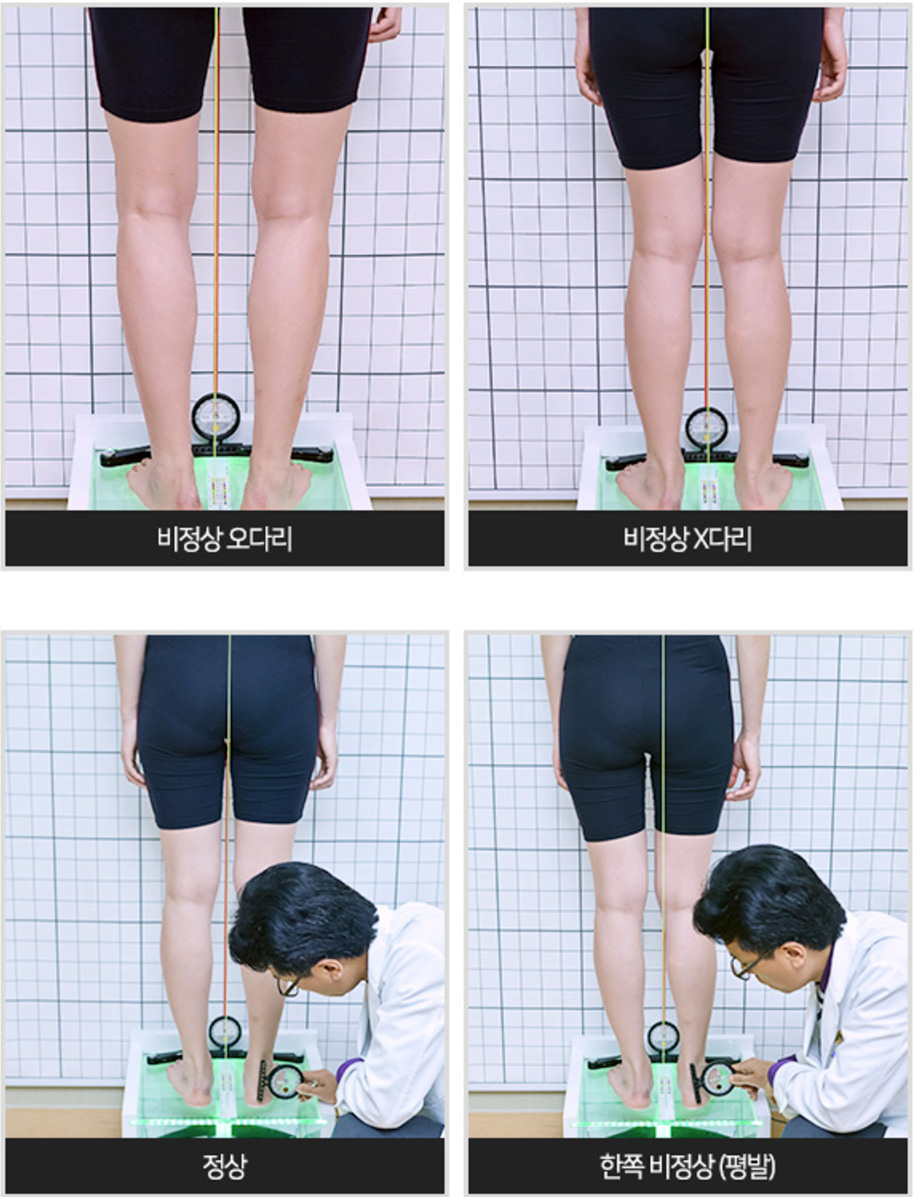
Foot and Ankle
In standing posture, the doctor performs foot and ankle joints examination focusing on the shape of the foot, the balance between the left and right, and the formation of the foot arch. The foot is the most basic structure that supports and maintains the weight of the human body. If the feet are off balance, the spine and pelvis can easily become deviated again even after they have been corrected. Therefore, feet are so important in the MBR treatments.
03
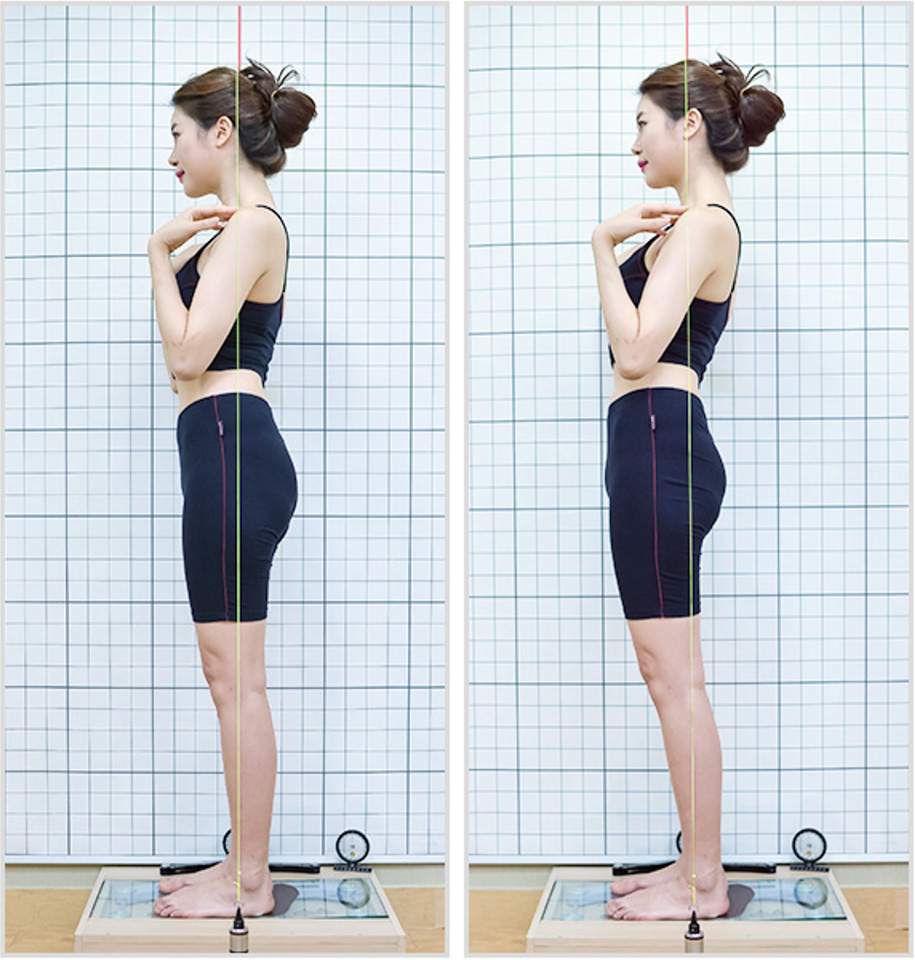

Lateral View
Posture examination of the lateral view can identify the interrelationship of each joint from head to toe. This test can identify the strength and weakness of the lower extremity muscles, the anterior and posterior pelvic tilt, core muscles, hunched back and head forward.
04

Flexion/Extension/Side Flexion
05
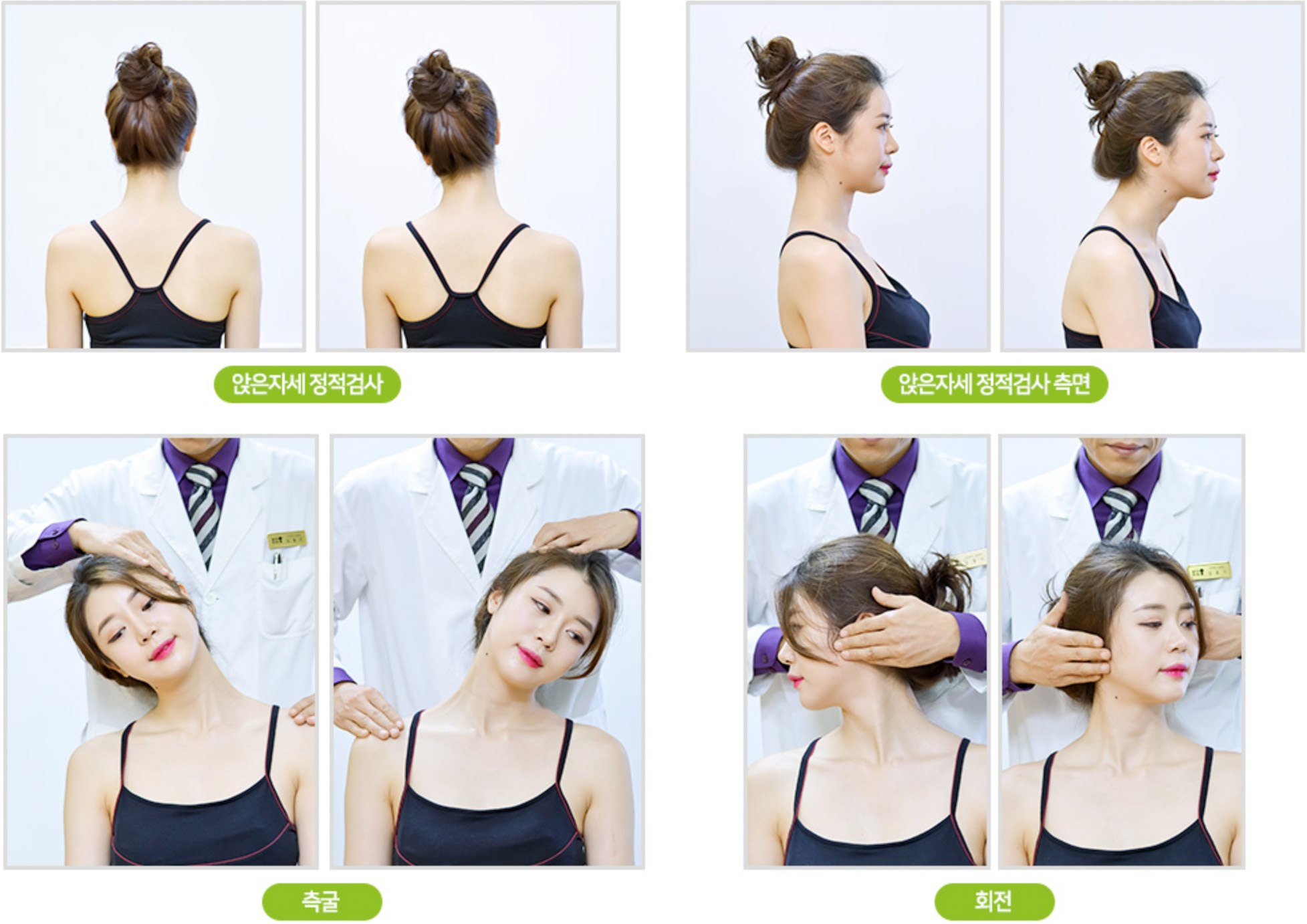
Seated Position 1
Sit-up posture screening is the first step of the cervical spine and neck ROM test. By comparing Flexion, Extension, Rotation and Lateral Flexion of the neck muscles, the doctor can check if the problem lies on the upper cervical or on the lower cervical spine and determine which spinal segment needs to be treated.
06
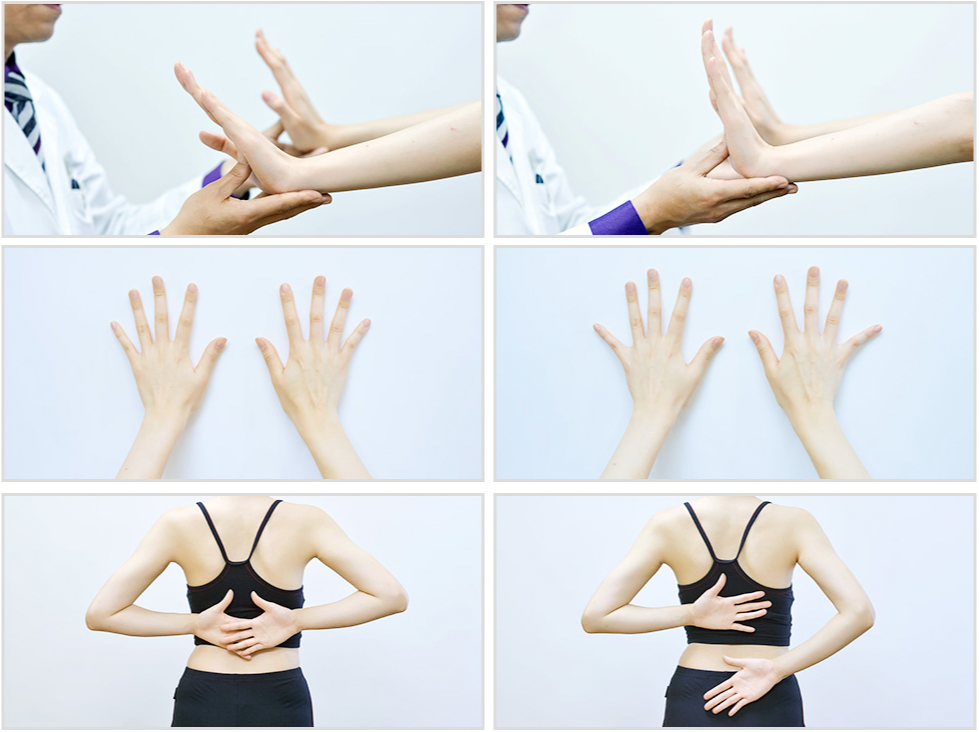
Seated Position2 : Upper Extremities
The upper extremity of the fingers, wrists, elbows, and shoulders motion examination checks the symmetry of the movements of each joint. In particular, the asymmetry of finger and wrist movement causes neck and shoulder pain and limitations of movement.
07
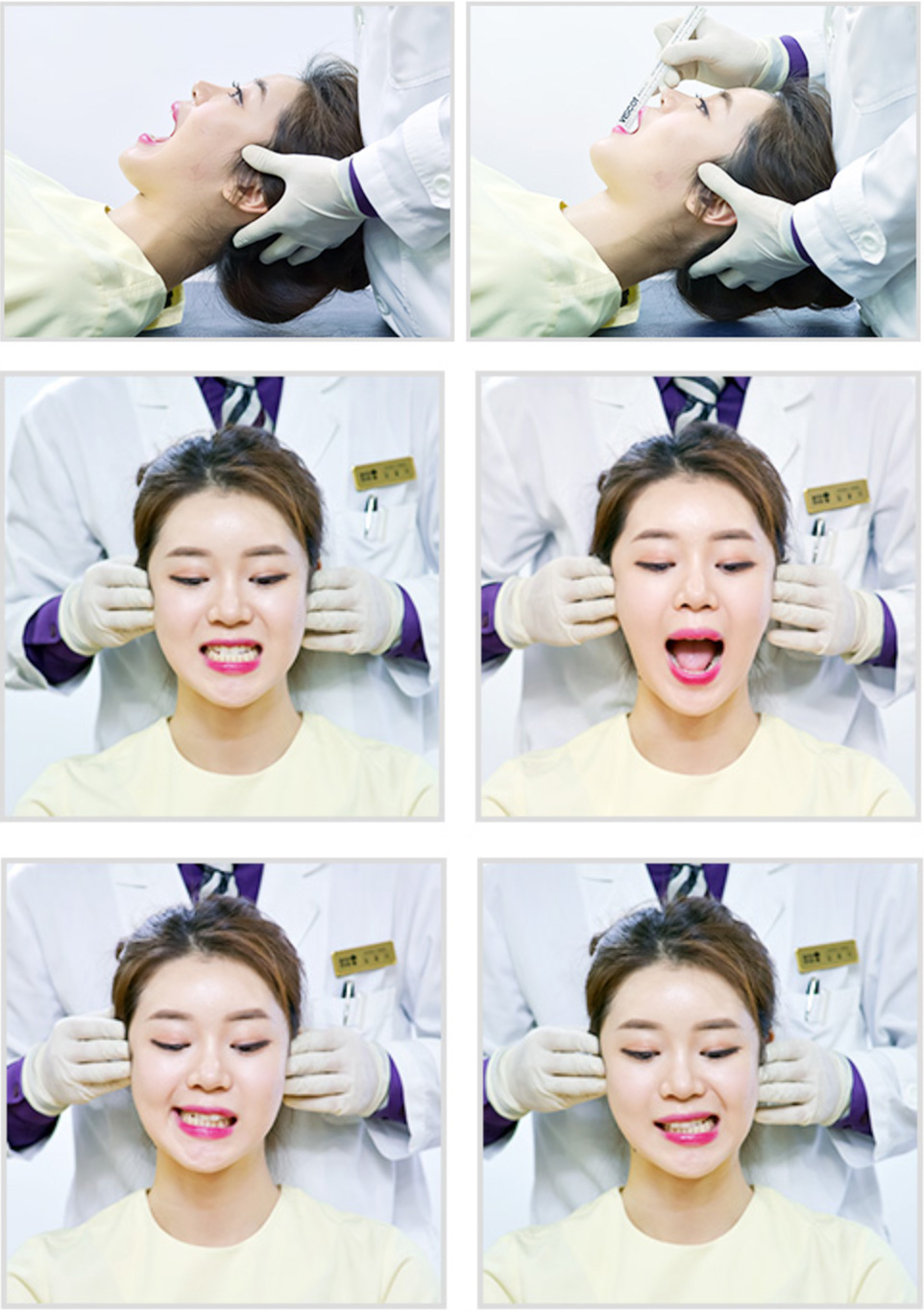
TMJ Assessment
The axis of TMJ movement is located on the C2, and the TMJ acts as a lever for the C2 which is the balancing axis of the human body, making the TMJ evaluation especially important. The TMJ evaluation focuses on the opening pathway, deviation, deflection, ROM, and the joint noises (e.g., clicking, crepitus) during opening.
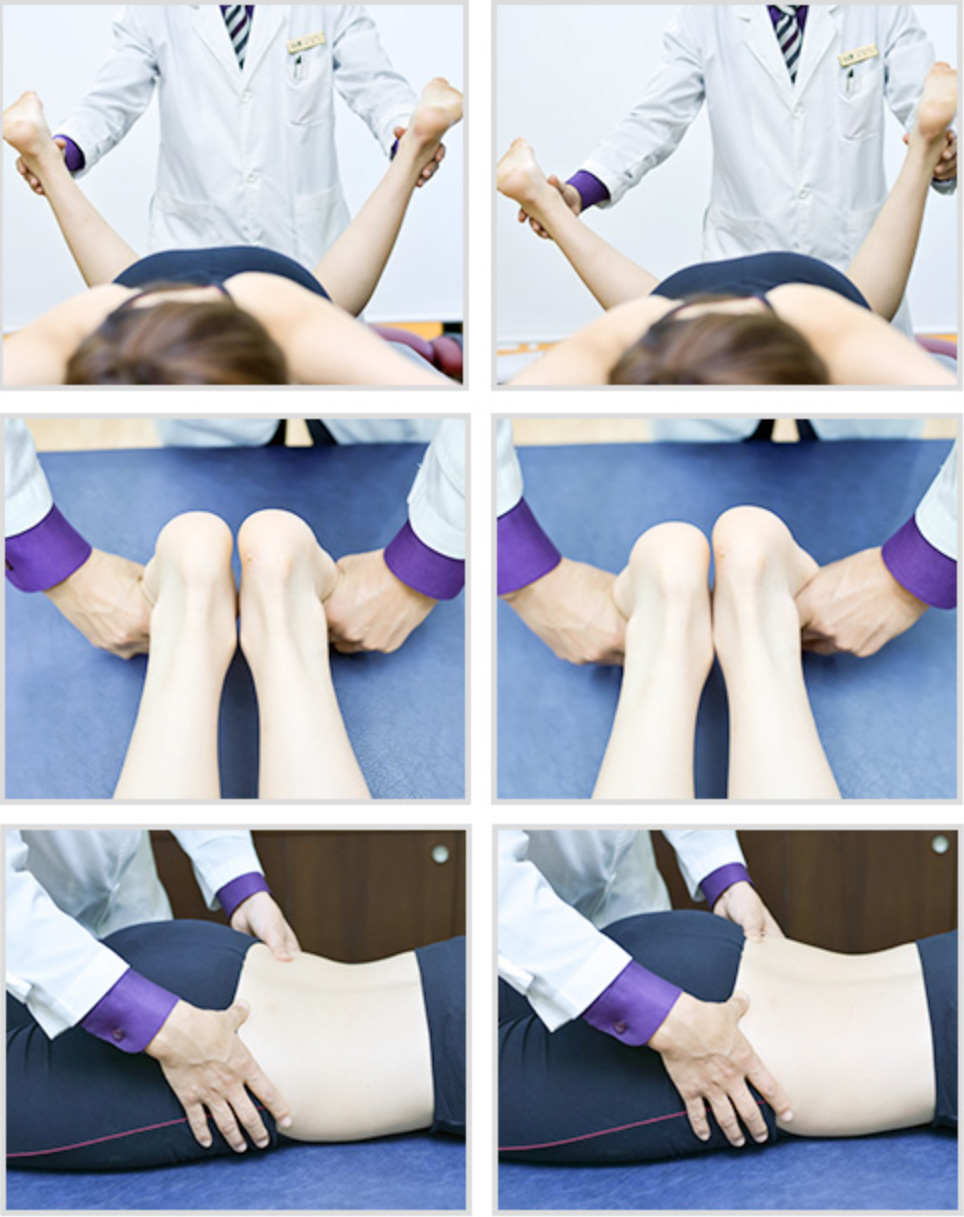
08
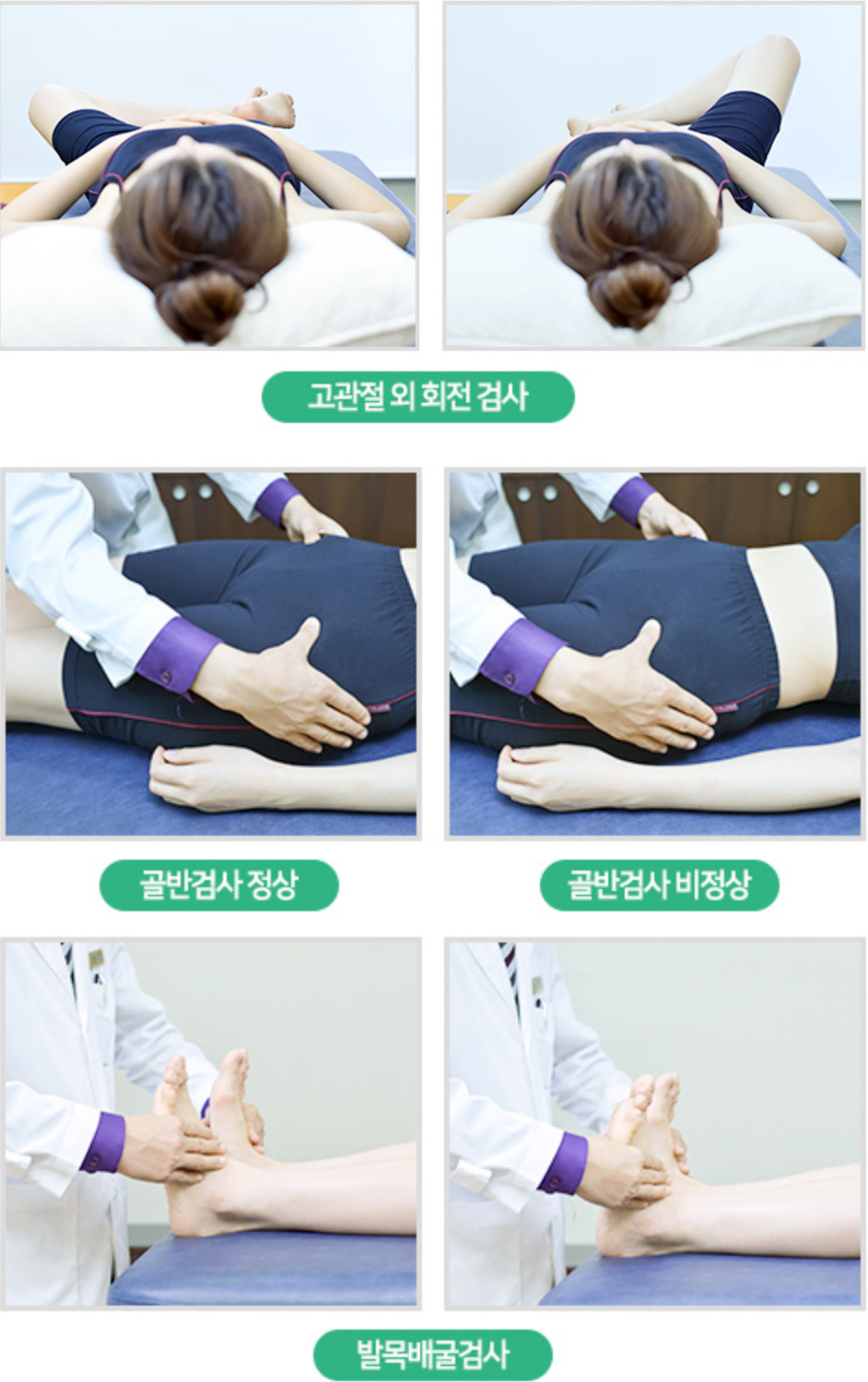
Supine Position
The supine posture test examines the lower extremities and pelvis, assessing pelvic problems and kinematic movements that may occur in the lower extremities. The degree of distortion of the pelvis, the balance of the left and right hips, the movement of the knee joint, and the balance of the left and right ankle joints are important.
09
Static Palpation
The static palpation is a simple way to check the mobility of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacrum when lying down, which allows to specify the location of incomplete dislocation or pain in the spinal segment.
10

Prone Position
The prone screening test focuses on the symmetry of the pelvic bone and sacrum, the movement of the hip joint, and the difference in length of the leg. The prone posture examination is an important test that can pinpoint the cause of the distortion in the spine by comparing its result with the result of the posterior posture examination.